How to tell if turmeric is synthetic?
How can you tell the difference between real and fake turmeric?
Is there fake turmeric? How to tell if turmeric is synthetic? How to distinguish real and fake turmeric? This article provides three methods to distinguish real and fake turmeric: solubility identification method, carbon 14 detection method and chromatography identification method.
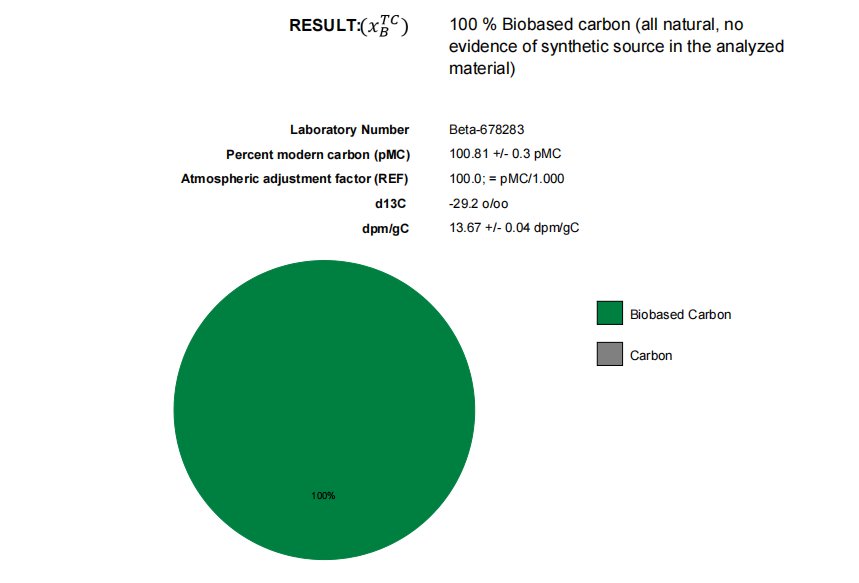
1. Carbon 14 detection
C14 detection can be used to distinguish natural and synthetic ingredients. Carbon 14 is a radioactive isotope that exists in all organisms in nature. Natural turmeric comes from plants, and the carbon 14 content in it is in dynamic equilibrium with the carbon 14 in the atmosphere, following the natural decay law. Synthetic turmeric is usually made by chemical synthesis, and its raw materials may not contain carbon 14, or the carbon 14 content is significantly different from the natural source. By measuring the amount of carbon-14 in a turmeric sample and comparing it to a known standard of natural carbon-14 content, it is possible to determine if the turmeric is synthetic.
2. Ingredient detection
Pure natural turmeric powder: the main ingredients are curcumin (C1), demethoxycurcumin (C2) and bisdemethoxycurcumin (C3).
Curcumin with artificial synthetic ingredients: may contain high concentrations of single curcumin (C1), or artificial synthetic pigments or other chemical components may be added.
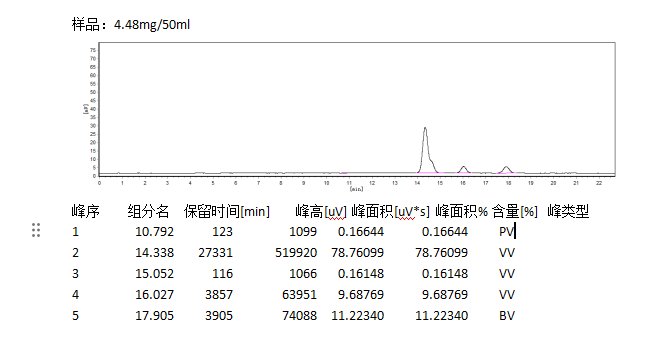
The composition can be detected by chromatography identification method. Select appropriate chromatographic analysis methods, such as high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), etc. to separate and process the samples, and then use the detector to convert the detected signals into chromatograms. By analyzing the retention time, peak area and other information of each peak in the chromatogram, it is compared with the standard chromatogram of natural turmeric.
The standard chromatogram of natural turmeric will have three peaks, C1, C2, and C3. If the chromatogram of the sample is highly similar to the standard chromatogram of natural turmeric, and the position and area ratio of each characteristic peak are consistent, it means that the turmeric may be natural; if there is a significant difference, it may be synthetic turmeric.

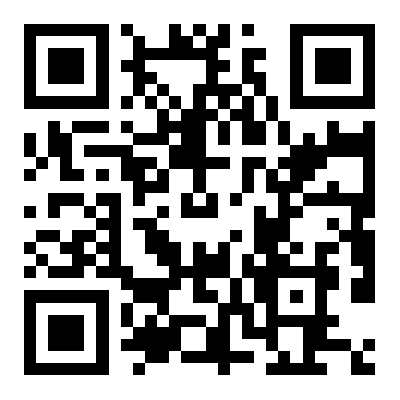
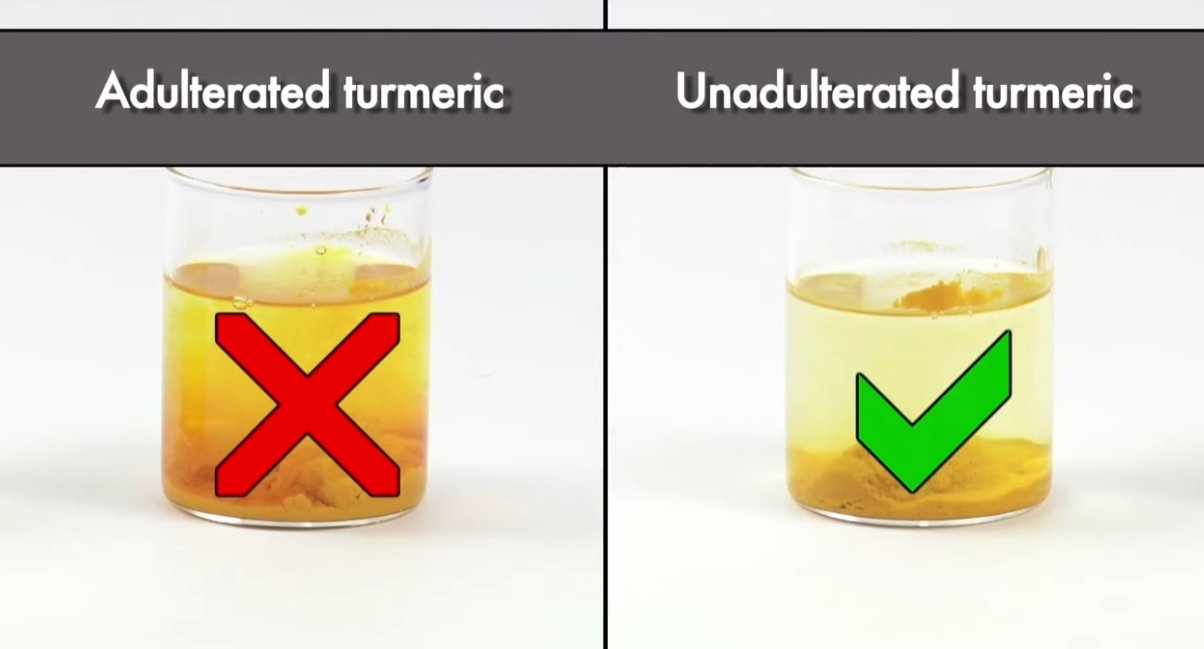
3. Solubility
Pure natural turmeric powder: dissolves slowly in water and may leave residue, because curcumin itself is insoluble in water.
Curcumin with artificial synthetic ingredients: may dissolve faster, have uniform color, and no obvious residue.